Step-By-Step Guide On How To File Taxes for Medical Clinic For USA Companies

Introduction
Filing taxes for a medical facility in America can prove quite perplexing owing to the industry's complex financial and regulatory landscape. Mastering one’s tax obligations is, therefore, paramount for compliance and fiscal stability. Let this guide to walk you through the essential steps to file taxes for a medical clinic, ensuring you are fully prepared and informed.
Step-By-Step Guide to File Taxes for Your Medical Clinic in the USA
The tax filing process for a medical clinic entails several pivotal phases, each intended to ensure adherence to federal, statewide, and community tax regulations. Here is a detailed breakdown of the process:
Step 1. Determine Your Clinic's Legal Structure
The initial step requires identifying your facility's legal structure, which will impact your tax duties. Common structures involve -
A sole proprietorship is the most elementary form, where the owner reports income on personal return.
A partnership encompasses several owners whereby profits and losses transfer to partners.
A Limited Liability Company provides liability protection and is capable of taxation as a sole proprietorship, partnership, or corporation.
A corporation (C-Corp or S-Corp) constitutes more complex structures with precise tax implications.
Each structure bears different tax rates and submission needs, so choose wisely, relying on your clinic's demands and future aims.
Step 2. Gather Necessary Documentation
Getting the proper documentation proves critical for accurate tax filing. Core documents include:
Step 3. Understand Tax Obligations

Familiarize yourself with the various tax obligations applicable to your clinic. Thoroughly researching regulations will ensure full compliance.
Step 4. Choose a Tax Filing Method
You have several options for completing your tax obligations:
Self-Preparation: Use tax software to guide you through regulations. Ensure you understand deductions to maximize savings.
Hiring a Tax Professional: A CPA or enrolled agent specializing in healthcare can provide guidance and ensure accuracy. Outsourcing provides peace of mind.
E-Filing: The IRS allows electronic filing to expedite the process and reduce errors. Many tax software options offer e-filing capabilities.
Step 5. Complete the Tax Forms

Fill out the necessary tax forms based on your legal structure and information collected throughout the year. Accuracy is key to avoiding penalties or audits.
Ensure you accurately report all income and claim eligible deductions, such as business expenses, employee wages, and healthcare-related credits, while reviewing the meticulously crafted forms to avoid mistakes that could lead to taxing penalties.
Step 6. Submit Your Tax Return
Once the forms have been thoroughly examined with an attentive eye, the completed tax return must be submitted before the fitting cutoff date. Typically, personal returns are expected by mid-April, while corporate filings may have differing deadlines depending on complex circumstances. Should more time be required, an extension can be applied to postpone remittance, yet estimated taxes still demand settlement to dodge penalties.
Step 7. Maintain Records

Following submission, retain records of returns and accompanying documents for no less than three years. Preserving records proves important for eventual reference and in the case of an examination. Systematizing files could also facilitate the process for the next season of taxes.
Things to Keep in Mind
Remain Informed: Tax laws are often in flux. Consistently update yourself on novel regulations that may impact your clinic.
Consult Experts: Engaging with a tax agency can furnish tailored counsel and ensure adherence to tax laws.
Plan for Estimated Payments: Should your clinic generate significant income, consider making quarterly provisional tax disbursements to avoid a massive bill at year's end.
Maximize Deductions: Be aware of all possible deductions accessible to medical clinics, encompassing apparatus purchases, employee advantages, and operational expenses.
Consider Retirement Plans: Proposing novel retirement plans can provide manifold tax advantages for both the clinical establishment and its staff members while also strengthening employee loyalty over the long haul.
Stay Structured: Get a system for arranging fiscal records, receipts, and documents throughout the yearly accounting cycle. This will facilitate a tidier submitting operation and diminish the risk of inaccuracies or errors.
Respect Deadlines: Be cognizant of all pertinent date restrictions for payments and filings, such as estimated quarterly installments, annual returns, or local prerequisites. Noncompliance can incur penalties and interest.
Communicate Obligations: Ensure employees comprehend their fiscal duties, particularly if they are independent contractors or earn bonuses and commissions. Supply them the proper documents and information to meet individual tax commitments.
Reductions and Incentives: Clinics may qualify for diverse credits and incentives, including the Small Business Health Care Tax Credit or the Research and Development Tax Credit. Consult experts to pinpoint ways to decrease liability.
Strategize for Growth: As the practice expands, think about how structural, geographical, or service modifications may impact your taxes.
Are You Wondering How to File Taxes for Your US Medical Clinic? Contact SamsCashFlow Agency!

For professional help with tax preparation and accounting for your medical facility, book a call with SamsCashFlow at https://www.samscashflow.com/#book. Their experienced team specializes in healthcare taxation, ensuring adherence and maximizing deductions. Call immediately to streamline your tax filing process!
Appendices:
Appendix 1:
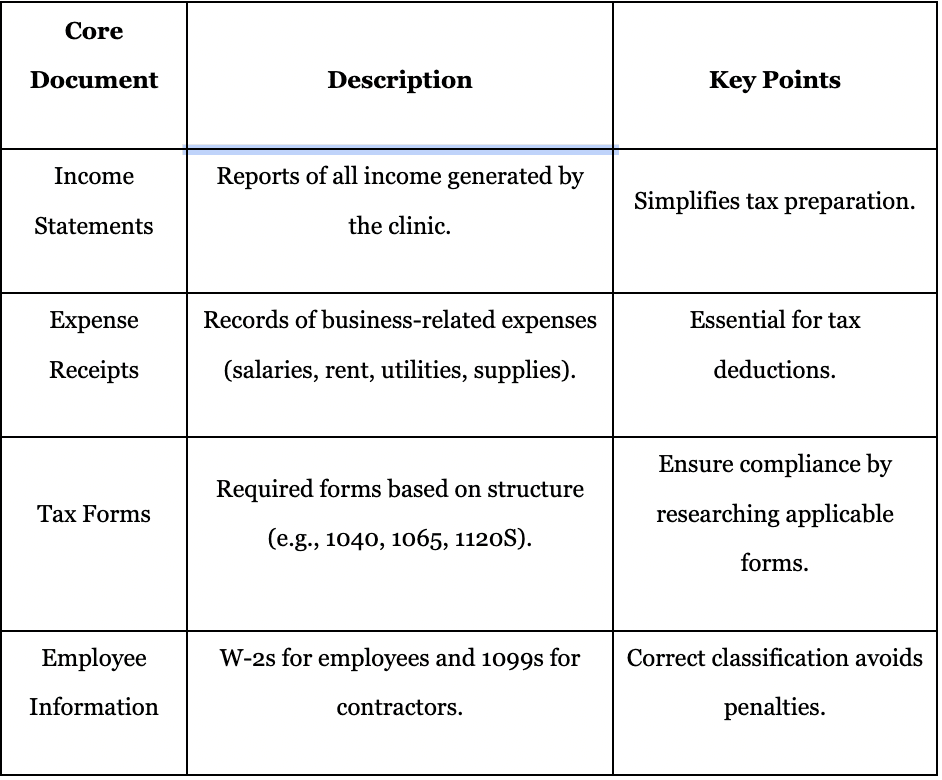
Core Document; Description; Key Points
Income Statements; Reports of all income generated by the clinic; Simplifies tax preparation.
Expense Receipts; Records of business-related expenses (salaries, rent, utilities, supplies); Essential for tax deductions.
Tax Forms; Required forms based on structure (e.g., 1040, 1065, 1120S); Ensure compliance by researching applicable forms.
Employee Information; W-2s for employees and 1099s for contractors; Correct classification avoids penalties.
Appendix 2:
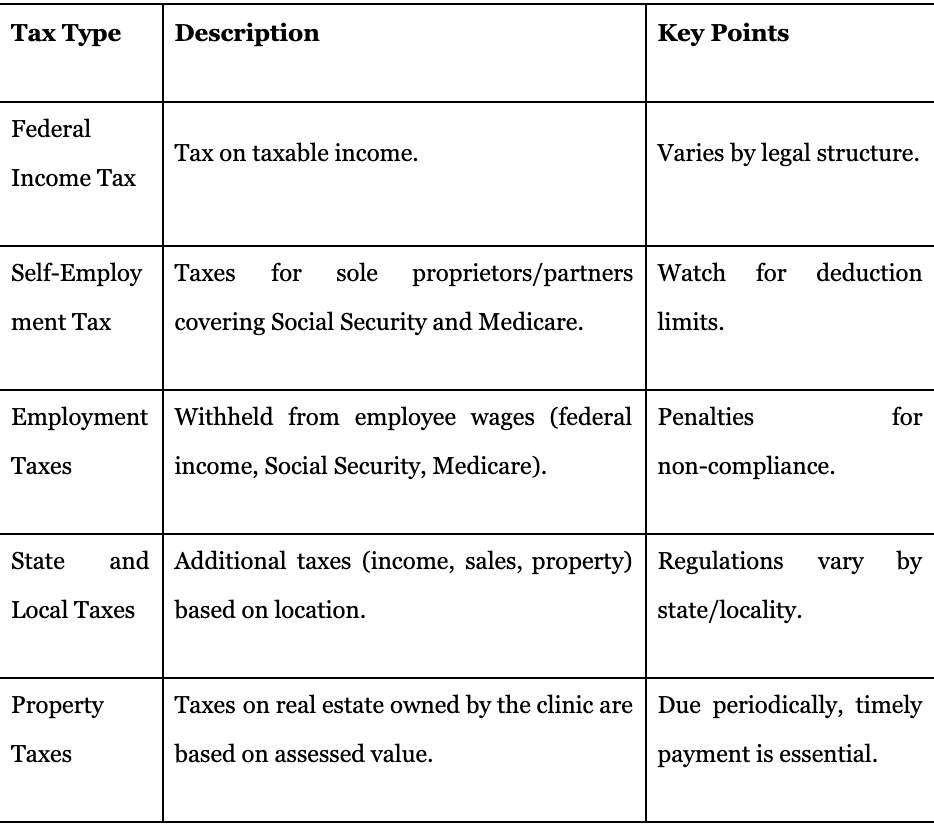
Tax Type; Description; Key Points
Federal Income Tax; Tax on taxable income; Varies by legal structure.
Self-Employment Tax; Taxes for sole proprietors/partners covering Social Security and Medicare; Watch for deduction limits.
Employment Taxes; Withheld from employee wages (federal income, Social Security, Medicare); Penalties for non-compliance.
State and Local Taxes; Additional taxes (income, sales, property) based on location; Regulations vary by state/locality.
Property Taxes; Taxes on real estate owned by the clinic are based on assessed value; Due periodically, timely payment is essential.
Appendix 3:
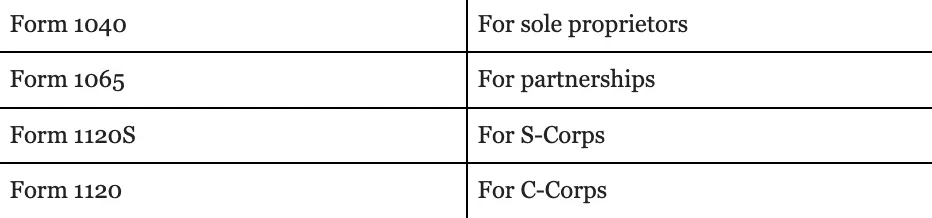
Form 1040; For sole proprietors
Form 1065; For partnerships
Form 1120S; For S-Corps
Form 1120; For C-Corps